CATEGORIES
CONTACT US
 Tel:+86-592 5745970
Tel:+86-592 5745970 Mobile:+8618059238601
Mobile:+8618059238601 Whatsapp:+8618059238601
Whatsapp:+8618059238601 Wechat:+8618059238601
Wechat:+8618059238601 Email:market@wondee.com
Email:market@wondee.com

The Ultimate 2025 Guide to Semi Trailers: Everything You Need to Know
Introduction to Semi Trailers
Semi trailers are essential to the global transportation industry. These non-powered vehicles attach to trucks and help move everything from groceries to heavy machinery across long distances. The concept dates back to the early 20th century, when freight hauling needed a more flexible solution than boxcars and wagons.
Over the years, semi trailers have evolved with technological innovations, becoming more durable, efficient, and specialized for different industries. Today, they’re the lifeblood of logistics, responsible for hauling over 70% of goods in the United States alone.
Different Types of Semi Trailers
Semi trailers come in various designs, each tailored to specific cargo types:
Dry Van Trailers
These are enclosed and versatile, perfect for general freight like packaged goods or electronics.
Flatbed Trailers
Open-deck trailers suited for oversized loads such as machinery or construction materials.
Refrigerated (Reefer) Trailers
Insulated and temperature-controlled units for perishable goods like food or pharmaceuticals.
Tanker Trailers
Designed to carry liquids—fuel, milk, chemicals—often with special linings for safety.
Lowboy and Double Drop Trailers
Ideal for transporting tall, heavy equipment. Their low deck height allows clearance under bridges.
How Semi Trailers Work
A semi trailer connects to a tractor unit using a fifth wheel coupling system, allowing it to pivot during turns. Air brakes, powered by the truck, stop the trailer. Lights, indicators, and other functions are powered via an electric cable connected to the truck’s system.
These trailers lack a front axle and rely entirely on the tractor for movement and steering, which gives them their "semi" designation.
Common Uses and Applications
Semi trailers are incredibly versatile. Here's where you’ll see them most:
Logistics & Freight: Transporting goods for retailers and manufacturers.
Construction: Carrying heavy machinery, steel, and concrete.
Agriculture: Moving livestock, grain, or farm equipment.
Oil & Gas: Hauling chemicals and drilling gear.
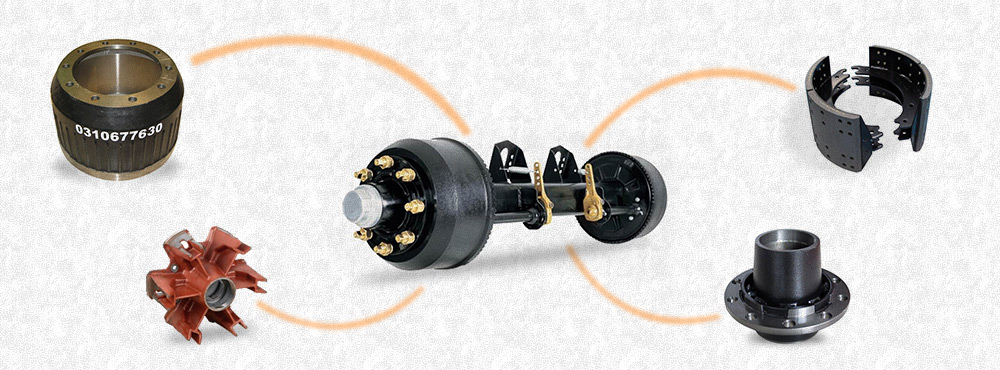
Key Components of a Semi Trailer
Every semi trailer has vital parts that keep it operational:
Axles and Suspension Systems: Support heavy loads and provide stability.
Flooring and Side Panels: Usually made of aluminum, wood, or composite for strength.
Electrical and Lighting Systems: Required for legal operation, especially at night.
Popular Semi Trailer Brands
Some of the top brands that dominate the semi trailer market include:
Great Dane
Utility Trailer Manufacturing
Wabash National
Fontaine
MAC Trailers
These companies are known for innovation, durability, and a wide selection of trailer types.
Key Components of a Semi Trailer
Understanding the main parts of a semi trailer helps ensure proper usage, maintenance, and safety.
Chassis
The chassis is the base frame that supports the entire structure. It provides rigidity and strength and is usually made from high-tensile steel or aluminum to handle heavy loads.
Axles and Wheels
Most semi trailers have two or three axles at the rear. These axles support the trailer's load and allow for smooth transportation. Wheels are fitted with heavy-duty tires to endure long hauls and varied terrains.
Suspension Systems
Suspension systems—either air-ride or spring—absorb shock and keep the cargo stable during transport. Air-ride systems are common for fragile or sensitive loads due to their smoother ride.
Braking System
Modern semi trailers use air brakes, which are powerful and reliable. These brakes are essential for maintaining control, especially when carrying heavy loads down slopes or in traffic.
Trailer Coupling and Kingpin
The kingpin is the pivot point on the trailer that connects to the fifth wheel of the tractor. This coupling is critical for safe towing and maneuverability.
Advantages of Using a Semi Trailer for Freight
There are many reasons businesses prefer semi trailers for their logistics needs.
High Payload Capacity
Semi trailers can carry up to 80,000 pounds (with proper permits), making them ideal for bulk transportation.
Cost-Effectiveness
Due to their large load capacity, businesses save on fuel, labor, and trips. One semi trailer can do the work of multiple smaller trucks.
Versatility Across Industries
From agriculture to retail to construction, semi trailers adapt to many cargo types. Custom trailer builds also allow for specialized transportation.
Common Industries That Rely on Semi Trailers
Semi trailers are essential in multiple sectors:
Logistics and Freight
Companies like FedEx, UPS, and DHL use semi trailers to move goods efficiently across long distances.
Agriculture and Farming
Farmers use flatbeds and refrigerated trailers to transport produce, grain, and livestock.
Construction and Heavy Equipment
Lowboys and drop deck trailers carry bulldozers, excavators, and building materials to job sites.
Licensing and Legal Requirements
Operating a semi trailer involves legal and regulatory considerations.
Commercial Driver’s License (CDL)
Drivers must have a valid CDL, often with additional endorsements for hazardous materials or double trailers.
DOT Regulations and Compliance
The U.S. Department of Transportation requires regular vehicle inspections, hours-of-service tracking, and safety protocols.
Weight Limits and Axle Configurations
Weight distribution is crucial to avoid fines or accidents. The Federal Bridge Formula dictates how much weight each axle can legally bear.
Maintenance Tips for Long-Lasting Semi Trailers
Regular upkeep prevents breakdowns and extends trailer lifespan.
Routine Inspection Checklist
Check the tires, brakes, lights, and connections before every trip.
Tire and Brake Maintenance
Ensure proper inflation and tread depth. Brake pads and drums should be inspected frequently for wear.
Electrical and Lighting Systems
Working lights and signals are essential for safety and legal compliance.
Safety Features and Innovations
Safety technologies continue to evolve in the semi trailer industry.
Anti-lock Braking Systems (ABS)
ABS prevents wheels from locking up during braking, reducing skidding and maintaining control.
Electronic Logging Devices (ELD)
These track driving hours and promote safer, more compliant trucking operations.
Rear and Side Underride Guards
These guards help prevent smaller vehicles from sliding under the trailer in a crash, significantly reducing fatal accidents.
Environmental Impact and Green Solutions
As environmental concerns grow, the industry is adopting greener practices.
Fuel Efficiency and Aerodynamics
Skirts, tails, and wheel covers improve airflow and reduce drag, saving fuel.
Electric and Hybrid Trailer Options
New models feature electric refrigeration units and regenerative braking to reduce emissions.
Regulatory Trends on Emissions
Agencies like the EPA and CARB are pushing for cleaner trucks through emissions standards and incentive programs.
Cost Breakdown and Financing Options
Purchasing a semi trailer is a major investment.
New vs Used Semi Trailers
New trailers offer warranty and latest tech, while used trailers are budget-friendly but may need repairs.
Leasing vs Buying
Leasing provides flexibility and lower upfront costs; buying builds equity and long-term savings.
Insurance and Maintenance Costs
Expect to pay for liability insurance, cargo coverage, and regular upkeep. These are ongoing costs to budget for.
Choosing the Right Semi Trailer for Your Business
Finding the right trailer involves analyzing your specific needs.
Factors to Consider
Load type, frequency of use, distance traveled, and legal requirements all affect your decision.
Customization Options
From lift gates to temperature control, semi trailers can be tailored to fit niche uses.
Best Brands in the Market
Well-known manufacturers include Great Dane, Utility, Wabash, and Fontaine, all known for reliability and innovation.
Future Trends in the Semi Trailer Industry
Exciting advancements are shaping the future of freight.
Smart Trailers and IoT
Sensors now track load weight, temperature, tire pressure, and location in real time.
Autonomous Trucking
While still in testing, driverless trucks are expected to revolutionize the supply chain in the next decade.
Regulatory and Market Shifts
New emissions laws, electric infrastructure, and e-commerce growth are influencing trailer design and operations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the difference between a semi trailer and a full trailer?
A semi trailer lacks a front axle and relies on the tractor for support, while a full trailer has axles at both ends and can stand alone.
2. How long is a standard semi trailer?
Most standard trailers are 53 feet long, though shorter lengths (28, 40, 48 feet) are also common.
3. What type of license is needed to drive a semi trailer?
You need a Commercial Driver’s License (CDL), often with endorsements for special cargo types.
4. How much weight can a semi trailer legally carry?
Typically up to 80,000 pounds gross vehicle weight without special permits.
5. How often should a semi trailer be inspected?
A pre-trip inspection is required daily, with more thorough inspections recommended every 3-6 months.
6. Are electric semi trailers available?
Electric models are emerging with features like battery-powered refrigeration and regenerative braking.
Conclusion
Semi trailers are more than just giant cargo carriers—they're the backbone of global trade and logistics. From hauling goods to powering industries, their design and versatility make them indispensable. With evolving technologies, regulatory updates, and sustainable practices, the semi trailer industry is well on its way to an even more efficient future.